& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
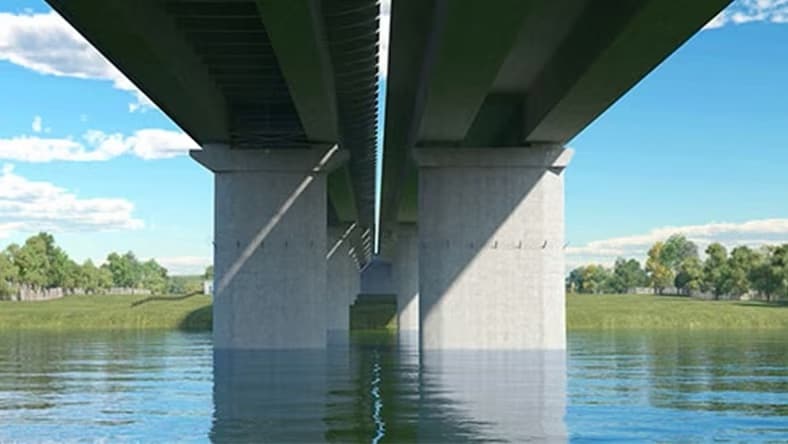
CAD (computer aided design) design is used in almost every industry, in projects as wide-ranging as landscape design (*), bridge construction, office building design and film animation (*) . With 2D or 3D CAD programs, you can perform a variety of tasks: you can create a 3D model of a design, apply material and light effects and document the design with dimensions and other annotations. With features such as point clouds (*), you can add real-life context to your drawings to create a digital twin or recreate physical objects in your designs.
*All links point to the US site.
CAD design is used by architects, construction managers and engineers and has replaced manual drafting. It helps users create designs in either 2D or 3D to visualise construction and enables the development, modification and optimisation of the design process. This helps designers make more accurate representations and modify them more easily to improve design quality.
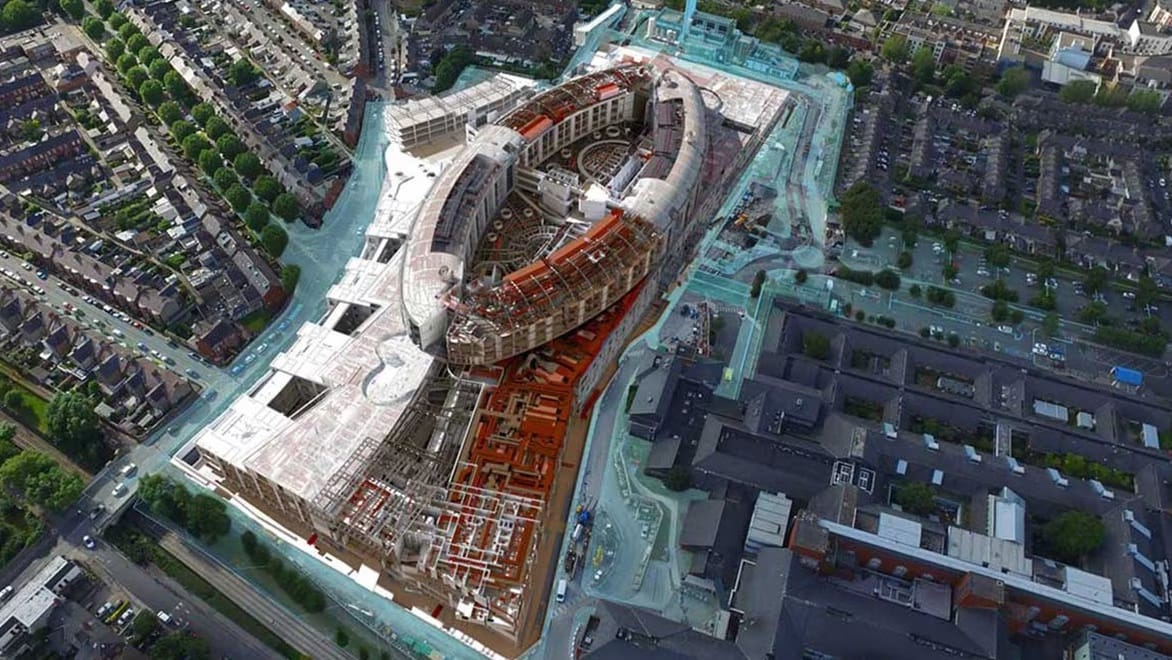
Building design is used from concept through to completion by professionals working in architecture, construction, MEP engineering and structural engineering and by building owners, operators and managers.
Infrastructure engineers and planners use CAD design tools to create intelligent 3D models and engineering drawings for land development, transportation (US Site), utilities, water and wastewater projects.
CAD design software is used by manufacturers and CAM professionals to machine, fabricate, 3D print, inspect and fabricate better quality parts, faster.
Throughout the development cycle, from concept to manufacturing, CAD design software is used to create consumer products, industrial machinery and building products and equipment.
2D and 3D CAD tools, with enhanced insights, AI-automations and collaboration features. Subscription includes AutoCAD on desktop, web, mobile and seven specialised toolsets.
Plan, design, construct and manage buildings with powerful tools for Building Information Modelling.
Best-in-class tool for 2D CAD drafting, drawing and documentation. Subscription includes AutoCAD LT on desktop, web and mobile.
Create, design and collaborate with AutoCAD Web. Experience the flexibility of accessing AutoCAD’s key design features from any computer or mobile device. Automate counting blocks, incorporate changes, display measurements and more.
Stratford Festival
By using AutoCAD and experimenting with other technologies such as 3D printing, Andrew Mestern of Stratford Festival delivers incredible set designs.
Image courtesy Stratford Festival.
Technica International
Automated product systems designer Technica International makes big gains in efficiency with Autodesk Product Design & Manufacturing Collection.
Image courtesy of Technica International.
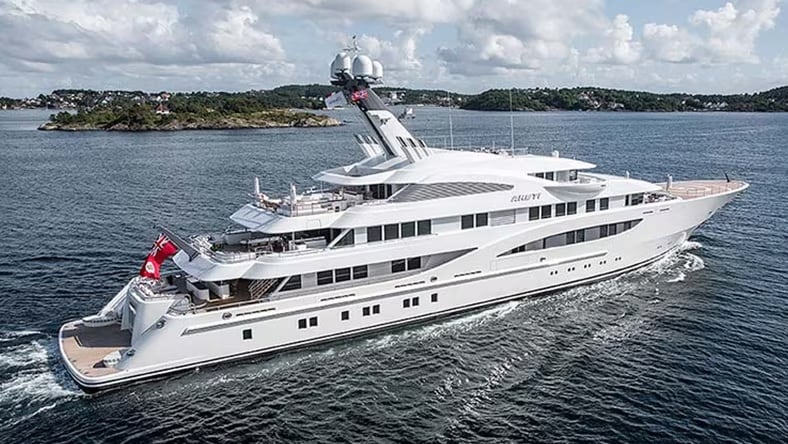
Winch Design
Discover how award-winning Winch Design relies on AutoCAD for its yacht designs, including the recent superyacht Areti.
Image courtesy of Tom Van Oossanen.
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computer technology by architects, engineers and others for design and drawing. Before CAD, design and drafting were done using pencil and paper. Benefits of using CAD design software include more precise drawing, ease for the designer to share plans with clients and third parties (such as general contractors and engineers) and secure archiving of past projects.
AutoCAD is the industry-standard software used by most civil engineers (US Site) and construction firms. Other commonly used software packages from Autodesk include Revit, Civil 3D and Fusion 360.
AutoCAD can be used for drafting and design projects that involve creation, editing, viewing or printing various types of geometric 2D and 3D entities. This includes projects like floor plans, construction layouts, building details, manufacturing drawings and layouts. Learn more.
AutoCAD is a desktop software application for 2D and 3D design and drafting used for creating blueprints and other engineering plans. AutoCAD is used in architectural drafting, civil drafting, mechanical drafting, electrical drafting, electronics, aeronautical drafting and more.
AutoCAD Mobile is a mobile drawing and drafting application that allows users to view, edit and share AutoCAD drawings via mobile devices. It can be used by general contractors and project managers with little to no experience with CAD across a wide range of industries, including architecture, engineering and construction, mechanical, electrical, plumbing and more.
AutoCAD’s native .DWG format and .DXF file format (US Site) are used in CAD design, but there are differences between the two vector image file types. The principal difference is that DWG (which stands for DraWinG) files previously only worked with Autodesk’s AutoCAD, while .DXF (meaning drawing exchange/interchange format) was developed to allow other CAD programmes to open and use information from the drawing file. There are now several free programmes that can open DWG files.
Some CAD programmes can’t import .DWG files, but they can import .DXF. If you’re a CAD user who doesn’t use AutoCAD, the ability to open and use the .DXF file in other CAD programmes is an advantage over the DWG.
Possible limitations of DXF in comparison to DWG are:
There are many benefits to using DWG files, including:
While some programmes may take time to learn, once mastered , CAD software can greatly enhance productivity and time to completion.
Advantages of CAD: