& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
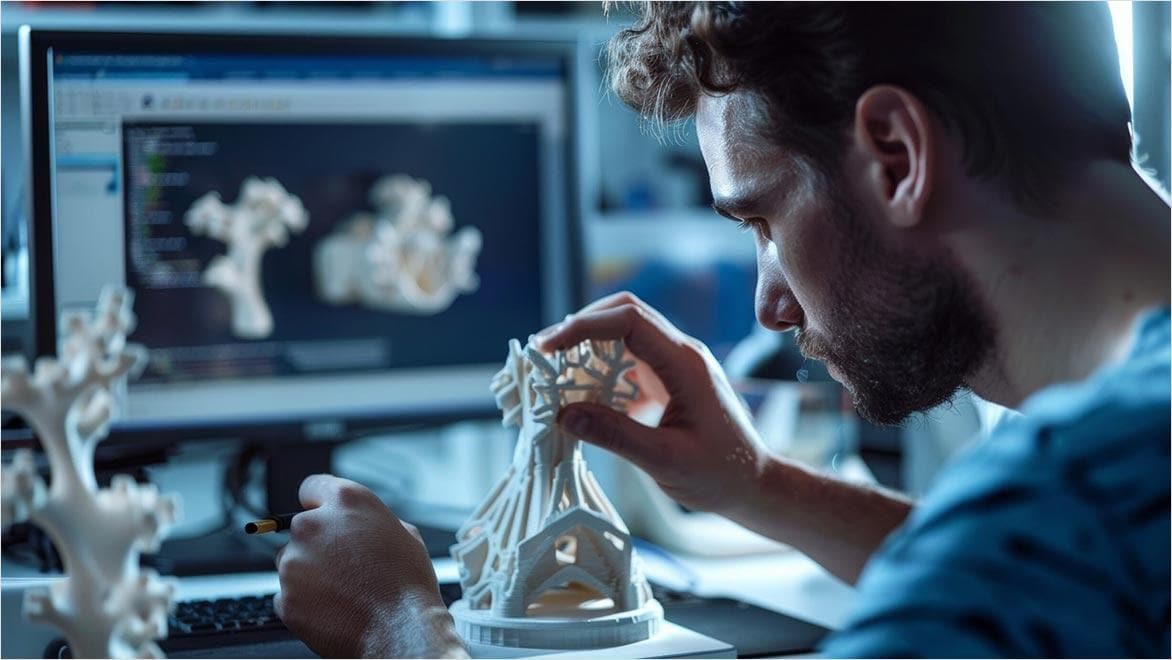
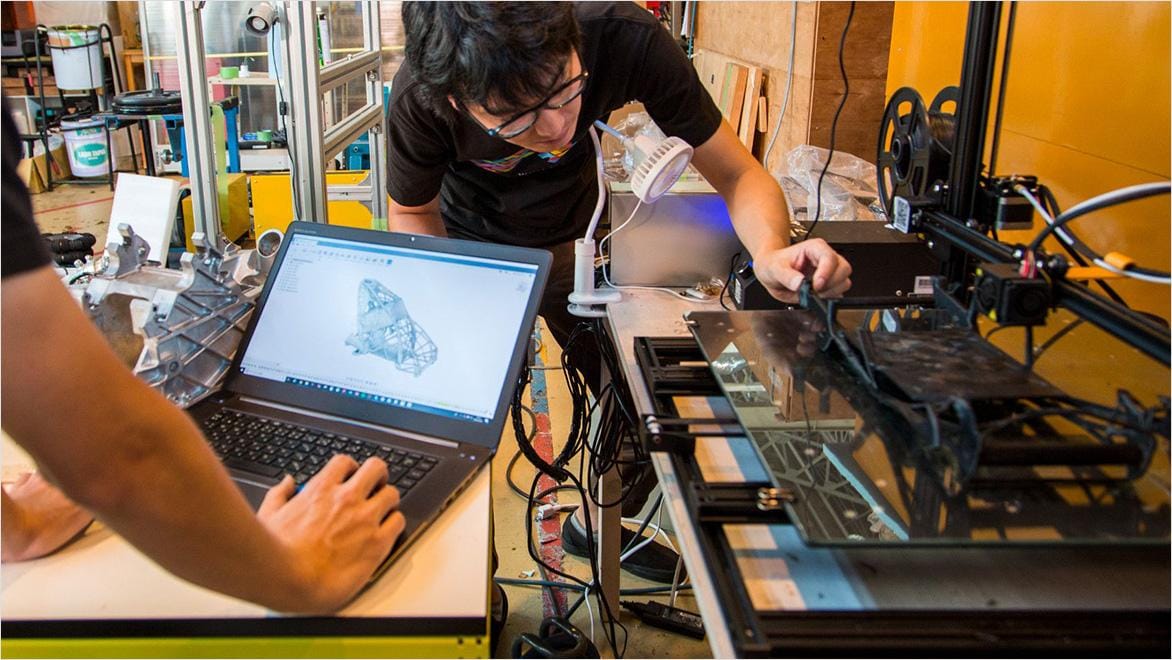
Rapid prototyping with 3D printing is the process of quickly creating physical models from digital designs to test ideas and improve them faster. Using tools like 3D modelling software and 3D printers, designers can turn concepts into physical objects in hours instead of weeks. This approach of 3D printing a prototype saves time and money by allowing for multiple test versions before final production.
The key benefits of rapid prototyping include speeding up the design process, reducing costs by using cheaper materials, and allowing for quick iterations to perfect the product. It also encourages creativity by letting designers experiment and innovate without wasting resources.
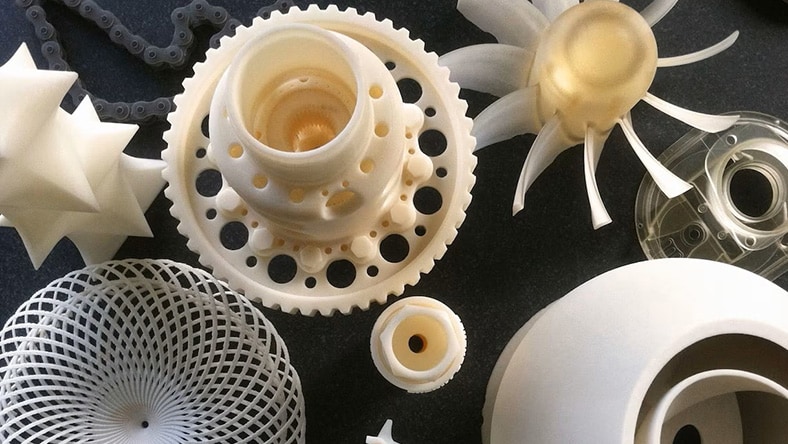
There are a variety of different types of rapid prototyping. Some of the most popular ones include:
Stereolithography (US Site) is an additive manufacturing method that creates a rapid prototype with 3D printing, by building up and curing a liquid photopolymer resin using an ultraviolet laser. This is then set in an ultraviolet oven.
Like SLA, selective laser sintering uses a laser to create a model. But it differs as a method of rapid prototype 3D printing by using a CO2 laser and powdered resin.
FDM is one of the most affordable types of rapid prototyping. It extrudes thermoplastic filament layer by layer to build up the 3D object.
Image courtesy of Formlabs.
2D and 3D CAD tools, with enhanced insights, AI-automations and collaboration features. Subscription includes AutoCAD on desktop, web, mobile and seven specialized toolsets.
Powerful product design and engineering tools for 3D mechanical design, simulation, visualisation and documentation.
Some of the most significant benefits of using rapid prototyping to 3D print prototypes are:
As the name suggests, rapid prototyping makes it possible to create prototypes quickly, and this can help to speed up the overall development process, and move from one iteration of a design to the next with ease.
Most 3D printing methods for rapid prototyping are relatively inexpensive, and can save on the labour costs of building prototypes using other means.
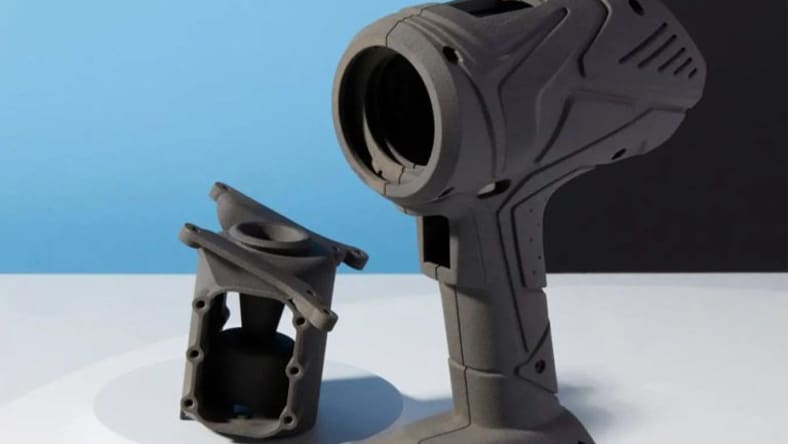
Rapid prototyping with 3D printing allows you to test out core design concepts and features before investing in production.
3D printed prototypes can be created quickly to be used to demonstrate design ideas at team meetings and investment meetings.
Bollywood is one of the most prolific film industries worldwide, producing an estimated 1500 to 2000 movies every year. These movies are famously known for their colourful aesthetics, heightened dramatics, musical numbers, and dance. They are fantastical yet culturally rich, telling stories about people, romance, legacy, and action.
For a typical Bollywood production, set designs, props and visual effects play a big role. Early on, filmmakers relied on practical effects teams to manually sculpt or fabricate props, often at a considerable cost of time, money, and resources. These days, the rise of digital tools and computer-aided design (CAD) has transformed the process, and the use of 3D printing for rapid prototypes of props has made it possible to realise creative visions faster, more affordably, and with better quality.
Instead of building physical scale models for set construction, filmmakers can save production time and effort with access to 3D prototype printing software like Autodesk’s Fusion, Maya, and 3ds Max. These tools are increasingly used in Bollywood films, improving overall quality and experience and enabling collaboration with skilled media and entertainment professionals across the world.
Technological advances like 3D printing are impacting the way teams, artists, and filmmakers create and distribute media, challenging professionals to find better, faster ways to bring their stories to life and achieve creative goals. But it’s all for the better. Props that used to take weeks can now take advantage of rapid prototyping with 3D printing to turn a sketch into a physical object.
Turning again to Bollywood, let’s look at how Autodesk helps conceptualise and execute ideas, including examples of how the software has been used for fast prototyping and other pre-production tasks in recent Bollywood hits.
In the Bollywood Adventure Epic, Kalki 2898 AD, a city fights against maxi-sized competitors for a chance at a better future. Autodesk’s Fusion was used to design its futuristic armour and costumes. With Fusion’s generative design (US Site) capabilities, the production team could simply input desired parameters for any object—such as weight, materials, and strength—and let the software generate multiple design alternatives so you get the perfect look before printing. Rapid prototyping allows designers to show multiple versions for a director to choose from easily.
Creating an immersive, large-scale environment is expensive. Fusion could help you realise your dreams and stay within budget through miniatures. By rapid prototyping and 3D printing your fantastical cityscapes and towering structures at a fraction of the size, you can simulate large-scale battles and expansive scenes without needing full-size set builds. It’s not only cost-effective but also allows you to film scenes that fit your movie’s aesthetic and meet practical requirements like functionality, stability, and mobility.
Using Fusion, you can transform everyday objects into futuristic designs or period pieces, and 3D printing prototypes allows you to test out multiple versions of a prop at a low cost. A basic helmet, for instance, can be redesigned to resemble a sleek space explorer's headgear with carefully placed 3D-printed modifications. The vehicles in Kalki 2898 AD were designed by overlaying mechanical elements and unique textures on a base model. Once the design was finalised, the add-ons were 3D printed with materials that made it easy to fashion lightweight, durable props that worked and looked realistic in action scenes.
The first step to using 3D printing in rapid prototyping processes is to create and design the model you will print from, using 3D CAD software like Fusion. Once this is done, you need to convert the model into the 3D printing format that you are using and feed it into dedicated 3D printing software that will turn the digital design into a blueprint for the 3D printer. Autodesk Fusion software makes this easy by offering an easy export process to the 3D printing tool of your choice. Once the design has been sliced into layers that can be understood by the 3D printer, it’s time to print the model. Afterwards, the 3D printing prototype can be refined manually to remove imperfections, via processes such as sanding and polishing.
Autodesk Fusion helps turn simple sketches into a physical model. Its parametric modelling features transform your idea while simulating the prop or object’s functionality. This ensures moving parts work as you expect before physical assembly begins, saving a lot of production time and ensuring it looks and works the way you need
With cloud-based collaboration, designers and engineers can work together no matter where they are. Designers can share their Fusion models with other team members, who can view, comment on, and even modify the designs in real-time. This speeds up design and production, reduces miscommunication, and ensures everyone is working from an aligned vision.
.
Find out everything you need to know about rapid prototyping and 3D printing, from its necessity for your product to non-negotiable steps and potential production costs.
Get all the details about 3d printing and rapid prototyping with Fusion and understand all the ways Fusion can support you through the development cycle.
Get familiar with Autodesk Fusion and its powerful extensions that offer a suite of tools for 3D printing prototypes, including electronics design, automated modelling, simulation, generative design, latticing, rendering, and more
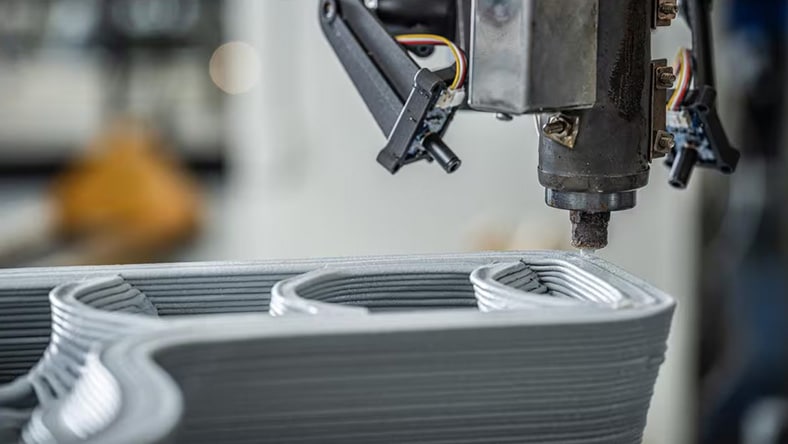
Rapid prototyping is a process of creating physical models from 3D computer-aided design (CAD) data. It works by using additive manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing.
3D printing rapid prototyping works by creating a 3D CAD model first, using software such as Fusion, and then converting this digital model into a format (such as STL) that can be interpreted by a 3D printer. The printer then builds up the 3D prototype layer by layer, at which point it can be set and finished by hand if necessary.
Rapid prototyping refers more broadly to the method and group of techniques for quickly constructing physical scale models of products and parts, so that they can be tested and refined before a full production run is made. Rapid prototyping is usually done with CAD software and a 3D printer.
Some of the key benefits of rapid prototyping with 3D printing are that it allows for quick iteration, testing, and refinement of designs, reducing time to market and development costs. Designers can test concepts in physical form, making it easier to spot flaws and make adjustments.
Industries like automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics , healthcare, and entertainment (such as films and video games) widely use rapid prototyping for design and product development.
Rapid prototyping via 3D printing is faster, more flexible, and less labour-intensive than traditional manufacturing, focusing on design validation rather than large-scale production.
There are many exciting innovations on the horizon for 3D printing prototypes, including the development of advanced materials that offer benefits such as additional strength, lightness and sustainability. AI-driven automation of the rapid prototyping process is also likely to play a significant role in future, while further advances in mass customisation for personalised products and parts are also expected.