& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
The Autodesk Fusion Manufacturing Extension unlocks advanced capabilities in Autodesk Fusion to help manufacturers make better use of machinery for metal-based additive manufacturing, CNC machining, and the nesting and fabrication of parts from sheet materials.
Choose from a range of flexible payment options to best suit your business needs or download a free 30-day trial of the Autodesk Fusion Manufacturing Extension today.
Automate manufacturing workflows to remove repetitive tasks, reduce errors and shorten the time to go from design to manufactured parts.
Access advanced tools to make better use of your machines, improve the quality and consistency of production, and increase profit margins.
Get flexible access to advanced manufacturing technology when and how you need it. Unlock more with technology that pays for itself in weeks.
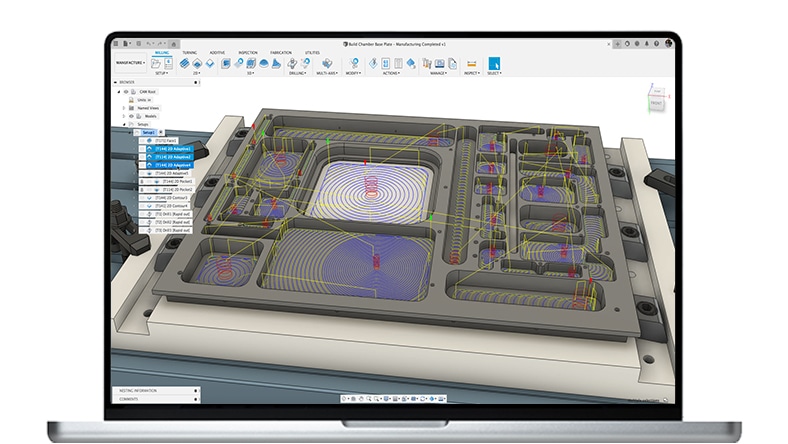
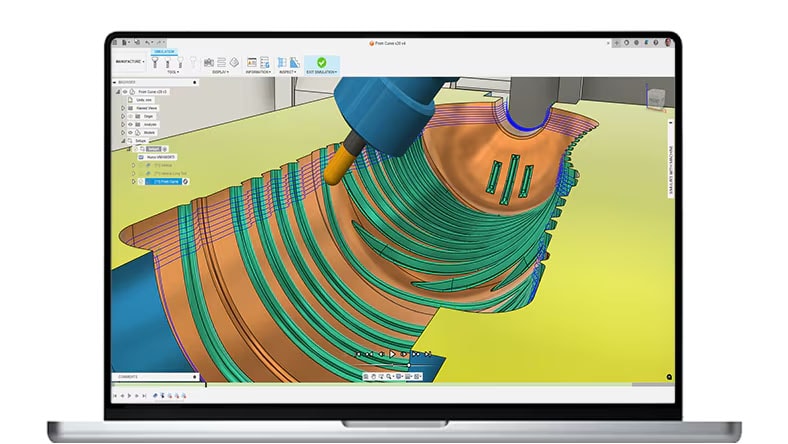
CNC MACHINING
Advanced CAM tools simplify the programming of 3-, 4- and 5-axis milling and turning, and generate high-quality NC code for mills and turn-mill machines.
CNC MACHINING
Program complex, feature-rich components with ease using intelligent whole-part strategies like steep & shallow, deburr, hole recognition and rotary.
CNC MACHINING
Speed up CAM programming with powerful modification tools that can turn a good toolpath into a great one – all without wasteful recalculation time.
CNC MACHINING
Use CAD-based probing strategies and spindle-mounted probes to automate part setup and measure components, helping you produce better parts in less time.
NESTING & FABRICATION
Convert 3D assemblies into precise 2D nested solutions ready for CAM programming, and automatically update nests if your original 3D design changes.
NESTING & FABRICATION
Smart nesting groups parts together based on thickness and other material-specific parameters giving instant insights for costing, quoting and ordering.
ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
Prepare 3D models for metal-based additive manufacturing with automatic part orientation, fully associative support structures and 3D printing file exports.
ADDITIVE MANUFACTURING
Use thermal simulation tools to validate the 3D printing process to avoid costly print failures and deliver better quality parts the first time, every time.
ADVANCED MANUFACTURING CAPABILITIES
Unlock additional capabilities for 3 to 5-axis CNC machining, sheet-based nesting and fabrication and metals-based additive manufacturing.
Includes advanced manufacturing capabilities:
*Requires an Autodesk Fusion subscription
AUTODESK FUSION + ADVANCED MANUFACTURING CAPABILITIES
Advanced CAD + CAM tools for manufacturers, machinists, engineers and teams needing precise high-performance CAM solutions.
Includes a subscription to Autodesk Fusion + advanced manufacturing capabilities:
We’ve teamed up with leading hardware, software and tooling companies to deliver even more value through partner technologies. Learn more about Autodesk partnerships (US site).
Break free from disconnected tools and fragmented workflows. Autodesk Fusion unifies CAD, CAM, CAE and PCB in one platform – boosting efficiency, cutting costs and streamlining production.
The Autodesk Fusion Manufacturing Extension unlocks more manufacturing functionality within Autodesk Fusion. The extension includes tools and workflows focused on subtractive CNC machining, sheet-based nesting and fabrication, and metals-based additive manufacturing.
Yes. The Autodesk Fusion Manufacturing Extension has the same capabilities as the previous Fusion 360 Machining Extension. Additionally, the Autodesk Fusion Manufacturing Extension also includes all features that were previously included in both the Fusion 360 Nesting & Fabrication Extension and the Fusion 360 Additive Build Extension.
A free trial is available for the Manufacturing Extension. Click here to download a free trial.
The Autodesk Fusion Manufacturing Extension can be accessed using different payment methods to suit your business needs, including daily, monthly and yearly options. Learn more about purchasing Autodesk Fusion extensions.
Yes. With the Autodesk Fusion Manufacturing Extension, you can design sheet metal parts and document flat patterns using 2D drawings and DXFs. You can also streamline the manufacture of your designs using CNC routers, waterjet, laser- and plasma-cutting machines. The Fusion Manufacturing Extension can help fabricators to:
Yes. The Autodesk Fusion Manufacturing Extension builds on the core capabilities of Autodesk Fusion to support many 3D printing/additive manufacturing applications and hardware types. Autodesk Fusion supports Fused-filament fabrication (FFF), Multi-jet Fusion (MJF), powder-bed and multi-axis deposition (such as directed energy deposition) in a wide range of metals, polymers and organics, and includes:
Yes. 3D printing and additive manufacturing are synonyms for the same process. Both terms reference the process of building parts by joining material, layer by layer from a CAD file.
Additive manufacturing is a process that adds successive layers of material to create an object, often referred to as 3D printing. Subtractive manufacturing, as the name suggests, is the opposite. Rather than adding layers, subtractive manufacturing involves removing sections of a material by machining or cutting it away. It can be carried out manually or, more commonly, by a process known as Computer Numerically Control (CNC) machining and takes many forms, such as milling, turning, turn-mill machining, wire-EDM and others.
Autodesk Fusion and the Manufacturing Extension have been built to create NC code that can be used by the vast majority of CNC machines. This includes 3- to 5-axis milling machines, lathes and turn-mill machines, as well as routers, laser-, plasma- and waterjet cutting machines that are typically used in sheet-based fabrication.
Unlike traditional CAD/CAM companies, Autodesk Fusion includes a free library of accurate 3D models of machines, 3D printing settings and post-processor files needed to export machine-specific G-code files. These have been developed in partnership with the machine tool manufacturers to provide increased accuracy and reliability.
No. The Fusion Manufacturing Extension is an additional cost option that requires an active subscription to Autodesk Fusion. Learn more about purchasing options for Autodesk Fusion and the range of Autodesk Fusion extensions.