& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Urban design is the planning of a city’s technical elements such as infrastructure, transportation, and street elements. Along with urban planning, urban design can give a place identity and shape its growth.
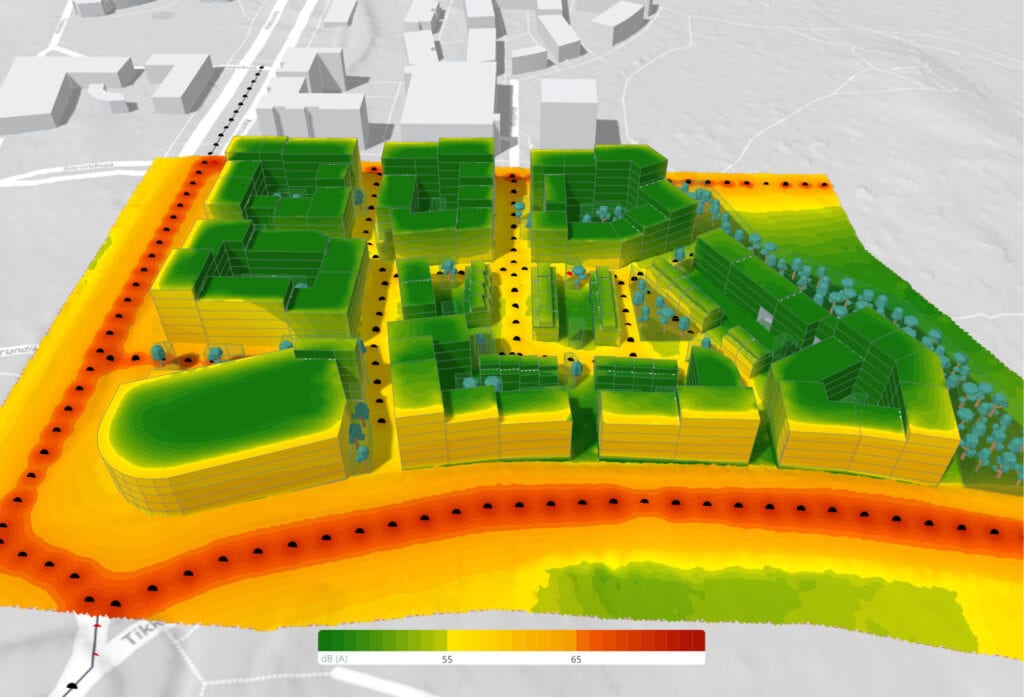
The scope of urban landscape design considers public spaces, buildings, streets, residential areas, landscapes, and more when planning what a new development or redevelopment could look like for a community.
Urban planning and design work together to maximize a city’s space and infrastructure and achieve the needs and goals of the community.
Urban planning and design typically share a common objective of shaping functional and resilient urban spaces, though they approach the task from different perspectives and at different scales.
Urban planners are responsible for planning large-scale residential, commercial, and industrial areas. They also establish policies and regulations for a city, helping establish building codes and plans for long-term land use that will further guide designers and architects.
Once an area has been planned, urban designers begin the technical work of planning for smaller, individual city features, such as public spaces, streets, buildings, and the interaction among all these elements. They are most concerned with the function and identity of a space.
In short, urban planning takes place at a more strategic level, whereas urban landscape design is more detailed, and focused on forming how the planned area will look and function. Urban planners and urban designers both work to create a city or community that is resilient, sustainable, and attractive to residents, workers, visitors, and businesses.
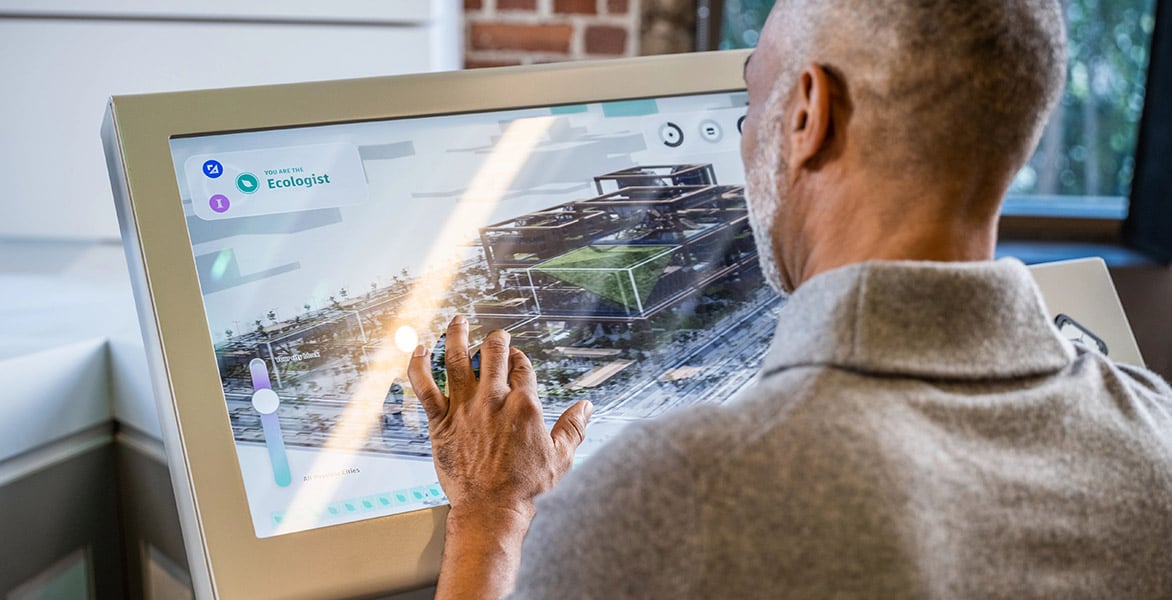
Urban design software makes it possible for urban designers and planners to envisage realistically how a space will look and work, and to incorporate geographic information systems (GIS) and building information modeling (BIM) data directly into their designs. 3D modeling urban planner software lets you see exactly how something will look—and, sometimes more importantly, to show others. Cloud-based features make it possible to collaborate in real time with other team members in the planning and design process and beyond. Finally, with urban design software, you can create reliable estimates of building costs and other related resource requirements.
Cloud software that offers powerful, easy-to-use, AI-powered tools for pre-design and schematic design. Making the right decisions in the planning phase has never been easier.
Cloud-based design co-authoring, collaboration, and coordination software for architecture, engineering, and construction teams. “Pro” enables anytime, anywhere collaboration in Revit, Civil 3D, and AutoCAD Plant 3D.
Coherent planning and design of cities and urban spaces shape the ways residents interact with and experience their surroundings. Below are some areas that urban planning and design practices can influence:
Urban design takes into account the real-life experiences of a community to provide a sense of space and identity. It also prioritizes universal access and ease of mobility, improving lives and inspiring new residents and visitors.
Adaptive design and planning can help cities plan for external factors, including recessions, social issues, and the effects of a changing climate.
Planners and designers can use technology and advanced urban design software to create ideas, iterate, and rapidly develop new models as feedback is applied to ideas.
Sustainable urban design considers what responsible, sustainable growth looks like, and the environmental impact of development on long-term living conditions.
Thoughtful consideration of factors s building orientation and placement of light sources helps create a sense of safety in a space.
A thriving community is one that attracts businesses, new residents, and visitors. Solid urban planning and design can lead to a significant return on investment for a city.
There are many different kinds of urban design—some examples include:
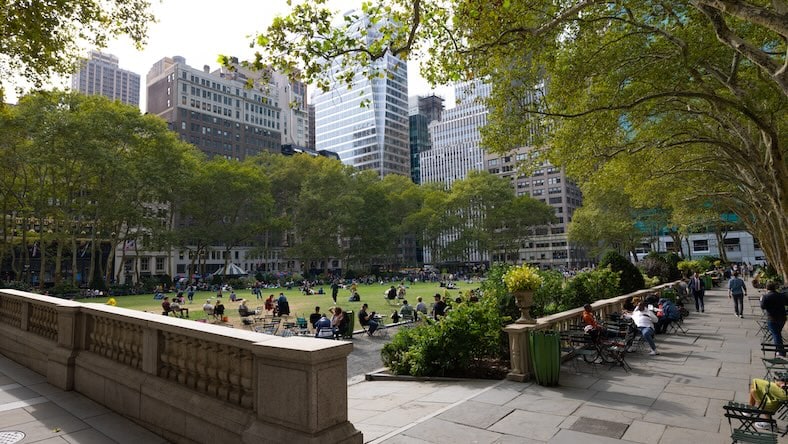
Well-designed public spaces can invigorate a community and become focal points for people to gather and relax.
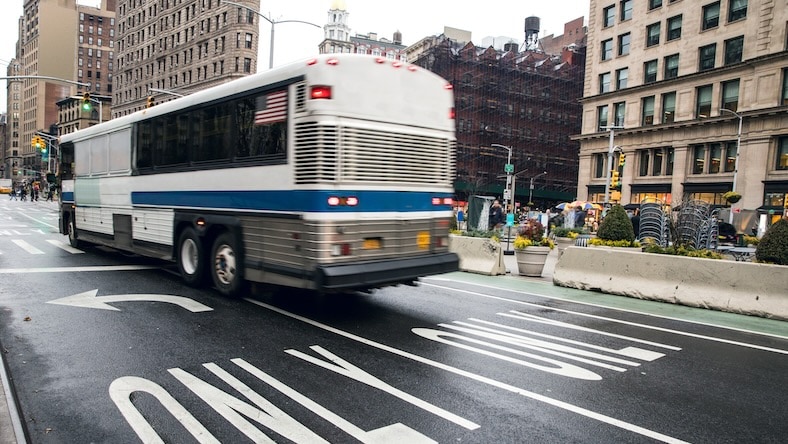
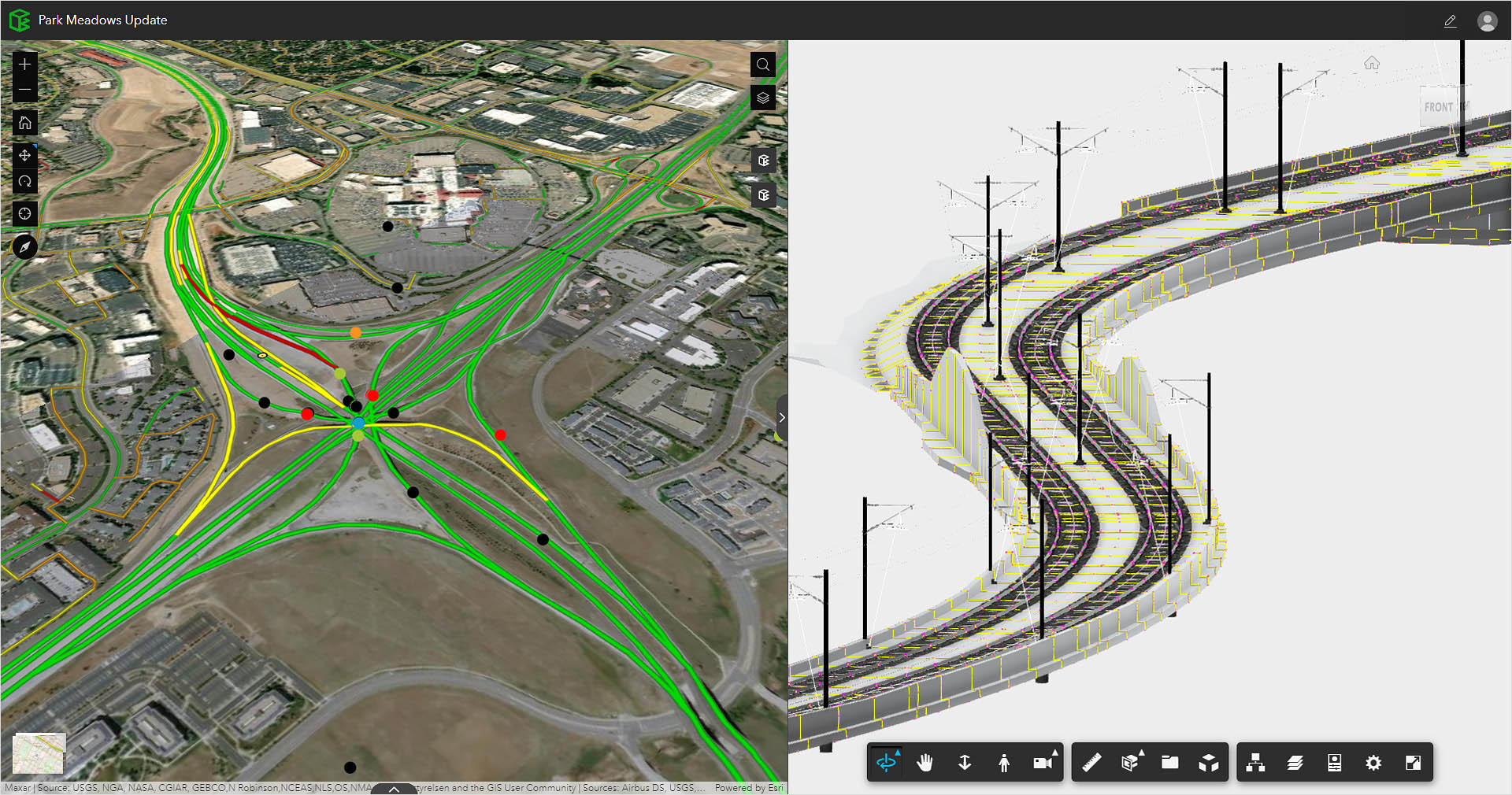
Everything from roads and pavement to cycleways, bus lanes, and metro rails needs to be designed to ensure that they work well for the city and its people.
In recent years, there has been a trend toward spaces offering a blend of residential, commercial, and leisure spaces. Urban landscape design and urban design software help ensure that these spaces are fit for purpose and coexist harmoniously.
There are many directions to take with any design, and parametric modeling makes it possible to try out different iterations quickly and efficiently. The parametric features within Autodesk’s software for urban planners and designers allow you to specify parameters for an object or design, such as spatial dimensions or materials, yielding different options that can be automatically created and incorporated into your urban landscape designs. You can easily experiment by changing building heights, urban density, utility planning, and more.
Skanska
A new “city within a city” is taking shape as plans for Oslo’s massive Hovinbyen residential and commercial project move toward final approval. Cloud-based urban design and collaboration tools have made it easier to balance diverse interests and negotiate a shared path to profitability.
GHD
In Abu Dhabi, real estate developer Tamouh Investments partnered with GHD to build a 272-hectare community called The Plantations. To create a dynamic sustainable urban design plan for long-term growth, planners turned to BIM and AR/VR with automation to develop several designs at once, making the process more efficient.
Image courtesy of GHD
Van Wijnen
Autodesk Research worked with Dutch construction company Van Wijnen to develop new residential layouts at an urban scale based on financial, sociological, and environmental considerations.
Learn how Dynamo can be used to implement generative design into workflows for urban planning projects.
Explore how AutoCAD Civil 3D software can help urban designers plan roadways, corridors, and curb transitions.
Read more about how generative design can be a financially smart choice for urban planners and developers.
Discover Autodesk Forma’s comprehensive, easy-to-use environmental impact analyses for urban planning and design.
Find out how BIM helped design a smart city development in Bordeaux, France.
Urban landscape design is one part of urban planning—a significant part. Urban design takes the broader idea of an urban plan and applies more concrete examples to the renderings.
Urban design provides models of how buildings will look, where public spaces can be positioned, and how the landscapes will work together. An urban design lays out vital infrastructure like streets in relation to transportation hubs and connects residential areas to parks. Design makes real how an environment or community would work, play, and live in a new development or redevelopment.
Urban planning is not the same as architecture. Urban planning takes a higher-level view of development, focusing on neighborhoods, zoning, building codes, and regulations.
Architecture is far more granular, focusing on a specific building, home, or block. Architects can use the parameters an urban plan establishes to create spaces that fulfill a customer’s needs while also meeting the expectations of the community’s or city’s broader plan.
Urban design focuses on how a particular urban space, or the spaces between urban buildings and elements, will look. Architecture emphasizes the appearance of one building, home, or commercial development.
In the hierarchy of urban landscape design, urban planning is the view from the air, a macro look at what will happen in the community. The urban design is ground level, with a real-world view of the streets, blocks, and neighborhoods. Architecture is micro, a close-up look at one specific project that will fit into its surroundings.
In urban planning, the primary elements for consideration are: