& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Mechatronics, also called mechatronics engineering is a multidisciplinary field that merges mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, computer science, and control engineering to design and develop innovative, intelligent systems. At its core, mechatronics combines these diverse engineering disciplines to create advanced systems capable of sensing, actuating, and controlling processes with exceptional precision and efficiency. These systems encompass a wide range, from everyday household appliances to complex industrial robots, and advanced medical devices.
The significance of mechatronics lies in its capacity to boost the functionality, performance, and reliability of products and systems. By harnessing the strengths of mechanical engineering, electronics, computer science, and control engineering, mechatronics engineering facilitates the development of smarter, more adaptable, and efficient technologies that cater to the needs of today's dynamic industries. This interdisciplinary approach fosters innovation and paves the way for cutting-edge solutions that greatly enhance quality of life and industrial productivity.
Mechatronics engineers design, develop, and maintain smart machines and systems by integrating mechanical, electrical, and control engineering principles. They create and test prototypes to ensure seamless system integration, develop automation solutions, troubleshoot issues, and manage projects through completion. They also engage in research and development to innovate and improve technologies, collaborate with interdisciplinary teams, and produce detailed documentation for their systems.
Mechatronics blends core components to create advanced systems, showcasing its functionality and applications.
These are the core of mechatronic systems, including motors, gears, and actuators that perform physical actions and translate control signals into movement or force.
Electronics control and power mechanical systems with sensors for measurements, actuators for commands, and circuits for signal processing and communication.
These regulate mechatronic devices using algorithms and feedback to ensure smooth operation of mechanical and electronic components. They include both hardware (microcontrollers, PLCs) and software (control algorithms).
Computers manage complex calculations, programming, and simulation of mechatronic systems, including PCs, embedded systems, and specialized hardware.
Sensors collect environmental data, and actuators use this data to make changes. Examples include cameras and temperature sensors for sensing, and motors and solenoids for actions.
Software is crucial for designing and controlling mechatronic systems, from embedded code to high-level applications for system management and customization.
Mechatronics engineering focuses on the integration of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, and software engineering while offering these benefits:
Mechatronics enhances precision in manufacturing and control processes by integrating advanced sensors and actuators, resulting in more accurate and reliable operations.
Combining mechanical and electronic systems improves overall efficiency, leading to reduced energy consumption and faster production cycles.
Mechatronics systems offer greater flexibility in design and function, allowing for easy adaptation to new tasks and changes in production requirements.
By integrating control systems with mechanical and electronic components, mechatronics enables higher levels of automation, reducing the need for manual intervention and increasing productivity.
Mechatronic systems find applications in various industries and engineering processes. Some common examples include:
Mechatronics is crucial in the automotive sector, improving safety and performance. Examples include anti-lock braking systems (ABS) that prevent wheel lockup during braking and electronic stability control (ESC) that enhances vehicle stability in challenging conditions.
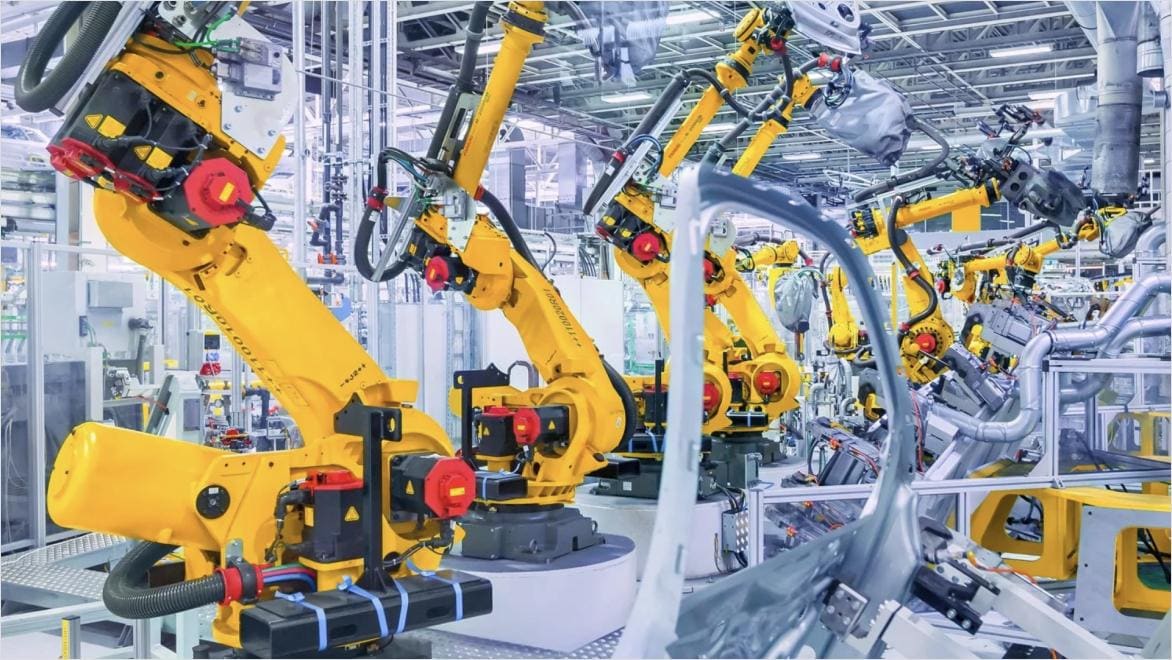
In robotics, mechatronics enables the development of both industrial and service robots. Industrial robots automate manufacturing processes with high precision, while service robots assist in tasks ranging from customer service to healthcare support.
Mechatronics enhances consumer electronics by integrating smart technology into everyday devices. Examples include smart home devices like thermostats and appliances that offer advanced features and connectivity for improved user experience.
In healthcare, mechatronics contributes to advanced medical devices such as surgical robots that assist surgeons with high precision and diagnostic equipment that provides accurate and reliable results for patient care.
The aerospace industry benefits from mechatronics through technologies like unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and sophisticated flight control systems that ensure stable and efficient aircraft operation, contributing to both commercial and defense applications.
Mechatronics enhances manufacturing and production with automation solutions such as precision CNC machines and automated assembly lines, improving production speed, consistency, and quality.
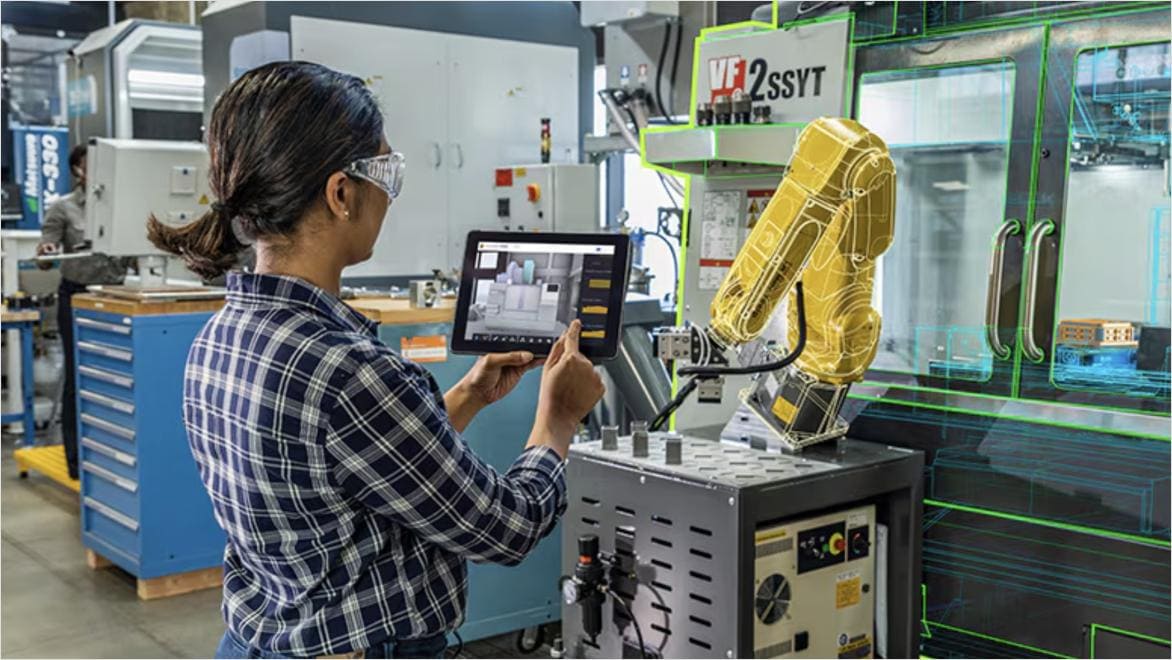
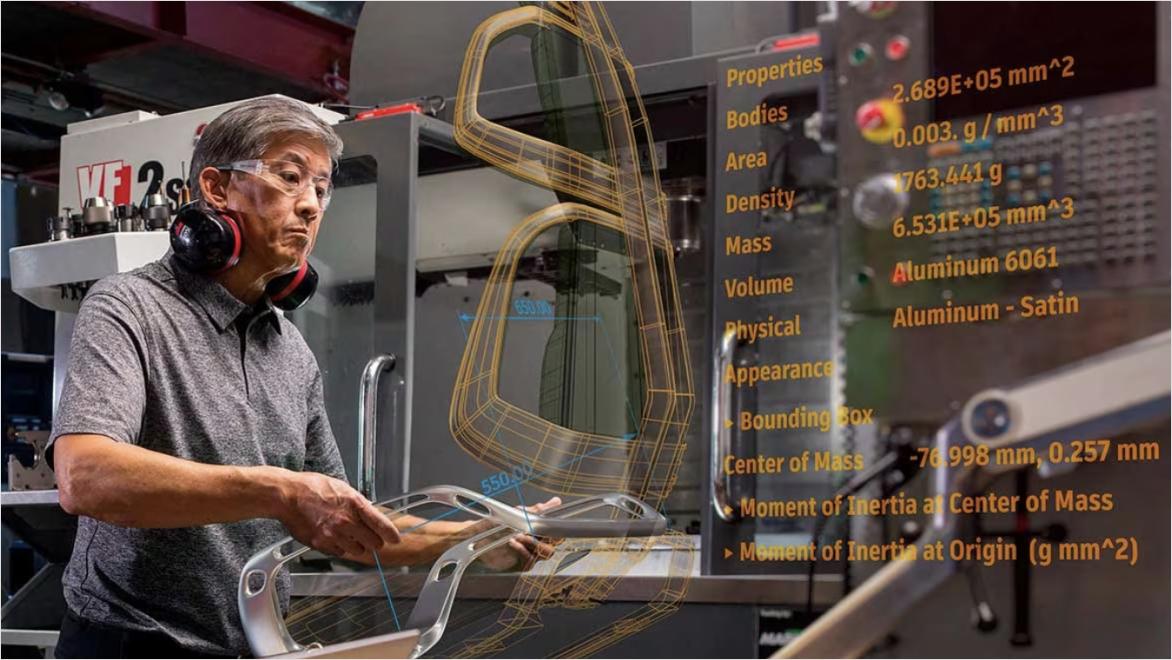
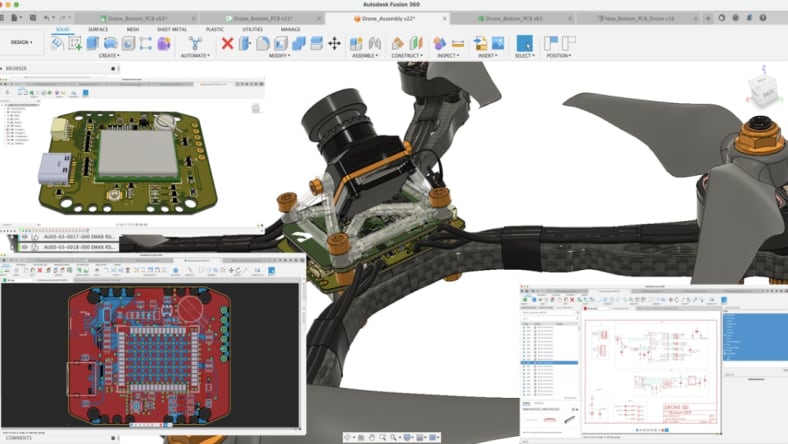
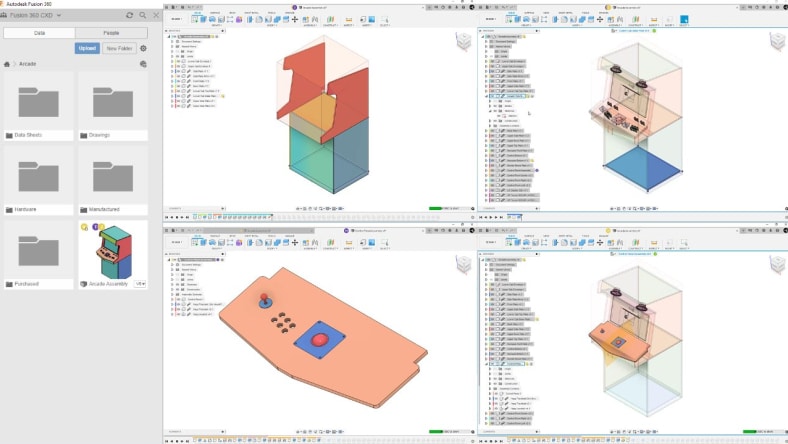
Autodesk Fusion plays a pivotal role in mechatronics engineering by offering an integrated platform for designing, simulating, and manufacturing complex systems. It enables seamless collaboration between mechanical, electrical, and software disciplines, facilitating precise parametric modeling, advanced simulations, and efficient production, driving innovation and optimization in mechatronic system development.
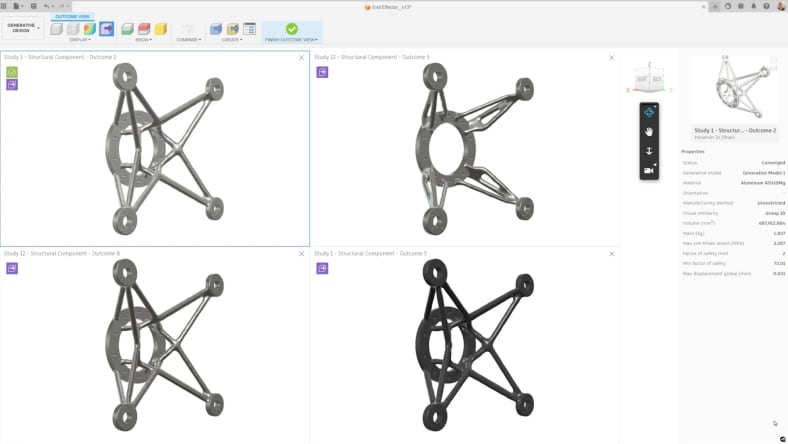
Optimize part design and performance with unlimited cloud solves for generative design, FEA, electronic cooling, injection molding, and more.
These are some top mechatronics engineering features in Autodesk Fusion.
Fusion provides a unified workspace for mechanical, electrical, and software design, enhancing collaboration and streamlining the mechatronics development process.
In Fusion, parametric modeling allows engineers to define relationships between components, enabling automatic updates and precise adjustments in mechatronic systems.
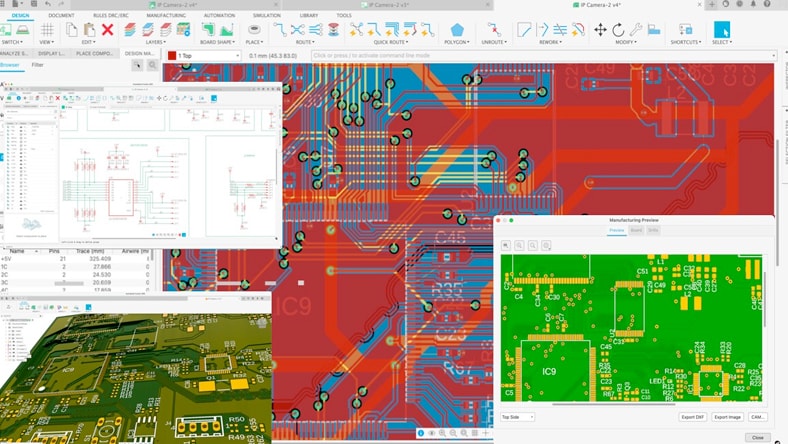
Fusion’s EDA tools facilitate the design and simulation of electronic circuits and PCB layouts, crucial for integrating electronics in mechatronic systems.
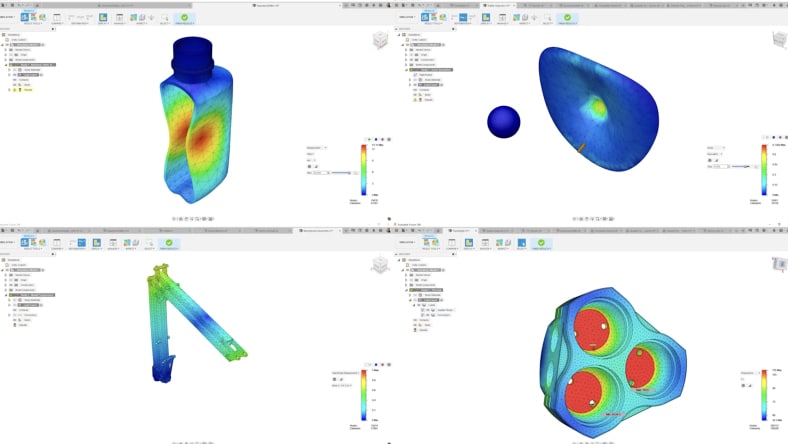
Fusion's simulation capabilities, including FEA and CFD, help analyze mechanical and thermal performance of mechatronic systems under various conditions, ensuring robust designs.
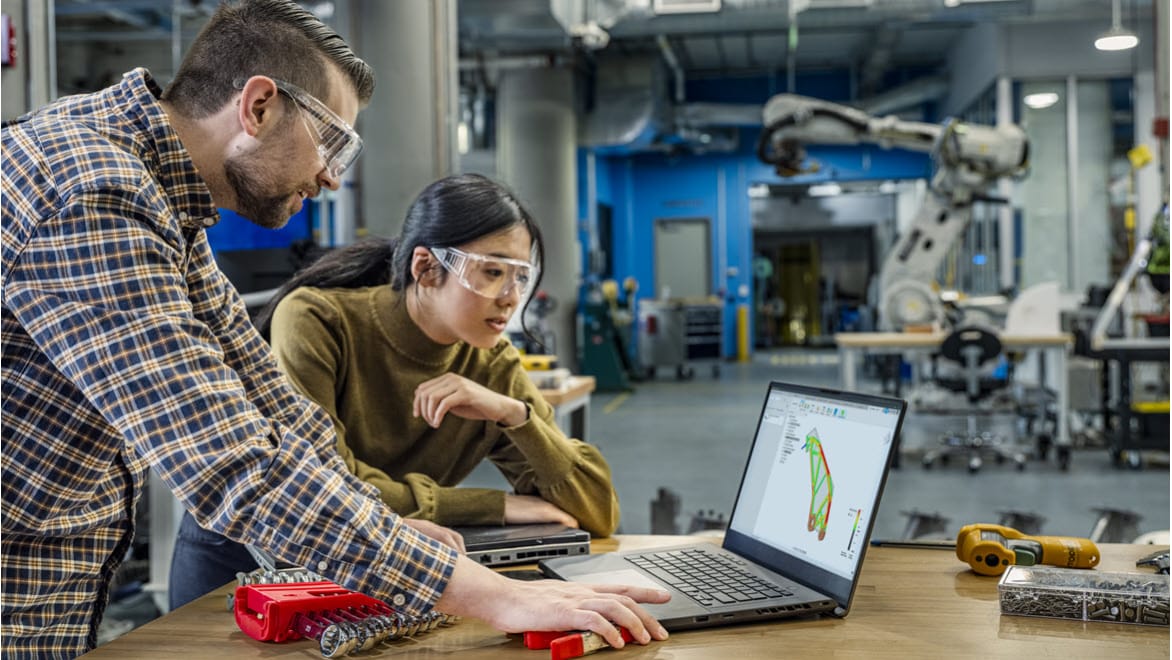
Fusion’s real-time collaboration features enable teams to work together on mechatronic projects, sharing updates, feedback, and revisions efficiently across disciplines.
Fusion integrates with manufacturing processes such as 3D printing and CNC machining, translating mechatronic designs into physical components with high precision.
Fusion’s generative design tools use algorithms to explore optimal design solutions for mechatronic systems, balancing performance, weight, and material usage.
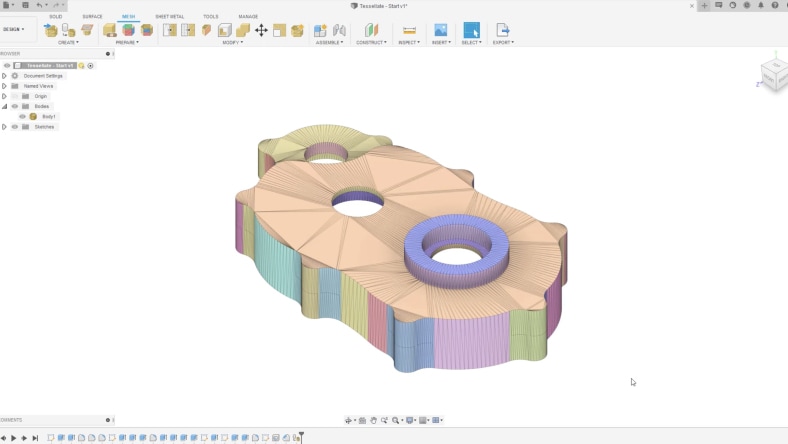
Fusion’s tessellation and mesh tools convert complex 3D models into editable meshes, essential for detailed analysis and simulation in mechatronics applications.
Explore mechatronics engineering, an interdisciplinary field combining mechanical, electrical, and control engineering to develop intelligent systems.
Discover how Fusion simplifies mechatronics by integrating mechanical, electrical, and software design. Elevate your projects with cutting-edge tools for seamless, optimized performance.
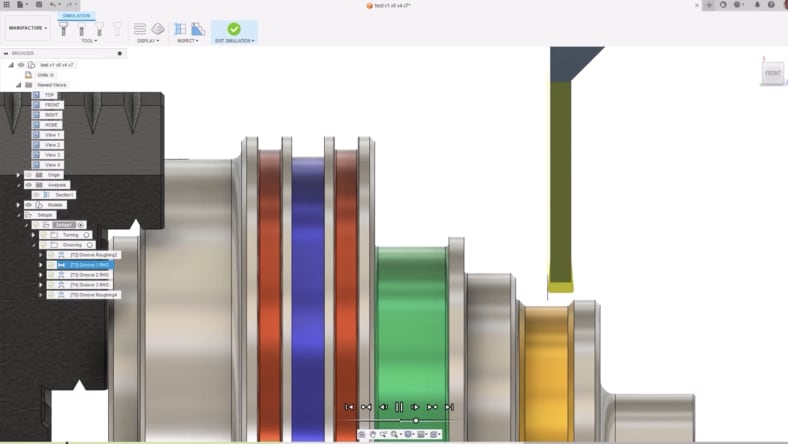
Unlock the power of mechatronics with Fusion's Simulation tools. Seamlessly validate, optimize, and perfect your designs for precision and performance using advanced simulation capabilities.
Unlock the future of automotive part manufacturing with mechatronics! Learn how Fusion’s integrated CAD, CAM, and CAE tools streamline design, testing, and production processes for maximum efficiency.
Fusion’s simulations optimize mechatronic systems by testing mechanical, thermal, and structural performance in a virtual environment.
Signal integrity is key in mechatronics for reliable communication between components. The Fusion Signal Integrity Extension, enables electromagnetic analysis of critical PCB signals, ensuring seamless performance.
The term "mechatronics" was coined in 1969 by Tetsuro Mori at Yaskawa Electric Corporation, initially referring to the integration of mechanical and electronic systems in industrial machinery. In the 1970s, the concept gained traction in Japan, improving manufacturing equipment and consumer electronics, driven by advancements in microprocessors and microcontrollers.
The rapid advancements in computer technology and control systems during this decade allowed for more sophisticated and precise control of mechanical systems. Robotics emerged as a key application of mechatronics, with significant progress in industrial automation and the development of robotic arms and automated assembly lines.
With the integration of advanced sensors, actuators, and real-time computing the field continued to expand. Mechatronics began to be applied in a wider range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. The introduction of CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) technologies changed the design and manufacturing processes, further blurring the lines between mechanical and electronic systems.
The growth of the internet and advancements in communication technologies led to the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), where mechatronic systems could be connected and controlled remotely. This era also saw the development of more complex and autonomous systems, such as drones, advanced robotics, and smart home devices.
Mechatronics has evolved with artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, creating smarter, adaptive systems. It now includes applications like autonomous vehicles, medical robots, smart factories, and wearable technology. AI and data analytics have further enhanced system efficiency and responsiveness.
Mechatronics enhances modern engineering by enabling the development of sophisticated systems that are more precise, efficient, and versatile. It improves automation and control in various applications, from manufacturing to consumer electronics. By combining mechanical and electronic systems, mechatronics facilitates the creation of intelligent products with advanced capabilities and adaptability.
Autodesk Fusion is a powerful tool in mechatronics, providing integrated solutions for 3D design, simulation, and manufacturing. It allows engineers to model mechanical components, simulate their behavior, and analyze how they interact with electronic systems. Fusion’s capabilities streamline the design process, optimize performance, and ensure that mechatronic systems function effectively.
Fusion’s parametric modeling allows engineers to define relationships and constraints between design elements, which is crucial for mechatronic systems. It enables iterative design adjustments and ensures coherence throughout the development process. For instance, in a robotic arm design, parametric modeling helps adjust joint angles and link lengths to optimize performance while maintaining structural integrity.
Autodesk Fusion offers several simulation features beneficial for mechatronics, including:
These tools help engineers validate designs, optimize performance, and ensure reliability in mechatronic systems.
Fusion supports the integration of electronic components through its PCB (Printed Circuit Board) design capabilities and electrical simulation tools. Engineers can design and simulate electronic circuits alongside mechanical components, ensuring seamless integration. This capability is crucial for developing systems where electronic and mechanical parts must work together harmoniously.
Mechatronics engineers have a wide range of career opportunities in various industries, including:
Mechatronics engineers can also work in research and development, designing and developing new technologies and products. They can also work in academia, teaching and conducting research in mechatronics and related fields. The diverse skill set of mechatronics engineers opens up numerous career paths, allowing them to contribute to a wide range of industries and technological advancements.
Autodesk Fusion aids in the development of robotic systems by providing tools for precise 3D modeling, motion simulation, and mechanical analysis. Engineers can design robotic arms, joints, and actuators, and simulate their movements and interactions. Fusion's parametric modeling allows for easy adjustments and optimization of robotic components to achieve desired performance and functionality.
Autodesk Fusion enhances collaboration through its cloud-based platform, which allows multiple users to work on the same project simultaneously. Features such as real-time data sharing, version control, and collaborative review tools enable teams to communicate effectively, share feedback, and make design changes collaboratively, streamlining the development process.
Control engineering is a critical component of mechatronics that involves the design and development of control systems that regulate mechatronic devices. Control engineers use a variety of techniques, including feedback control, feedforward control, and model predictive control, to design control systems that ensure smooth operation of mechanical and electronic components. By implementing these control strategies, engineers can achieve precise regulation of system behavior, optimize performance, and enhance the reliability of mechatronic devices. Control engineering is essential for applications ranging from industrial automation to autonomous vehicles, where accurate and responsive control is paramount.