& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Concrete design refers to the process of planning, analyzing, and structurally designing structures or elements made primarily of concrete, a versatile and widely used construction material.
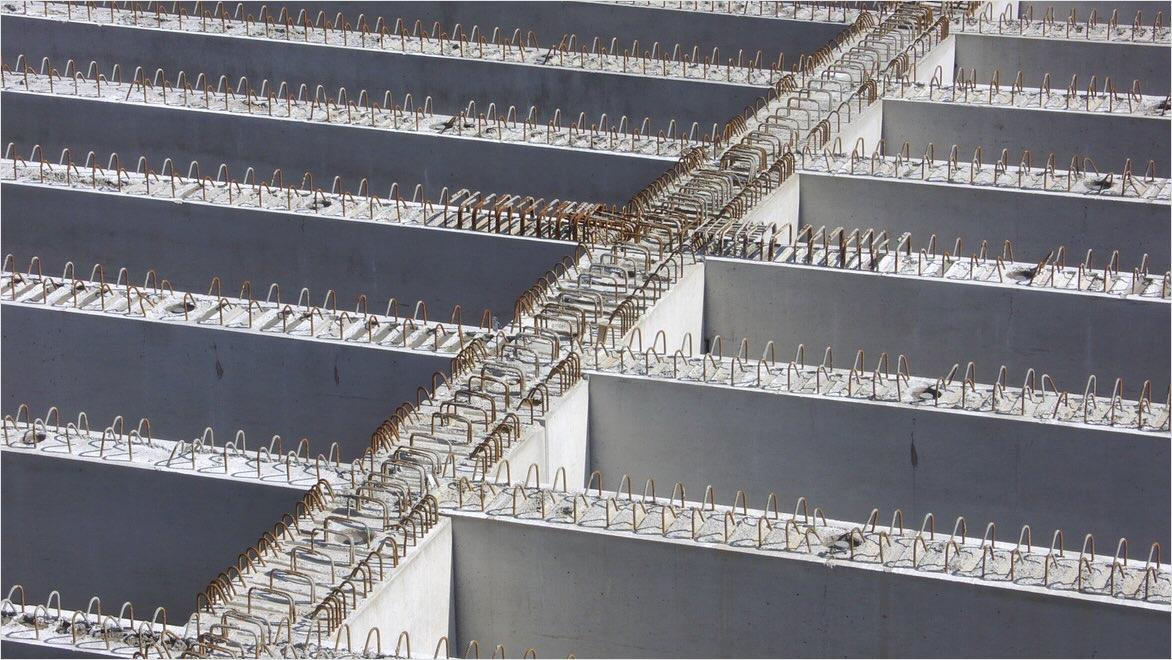
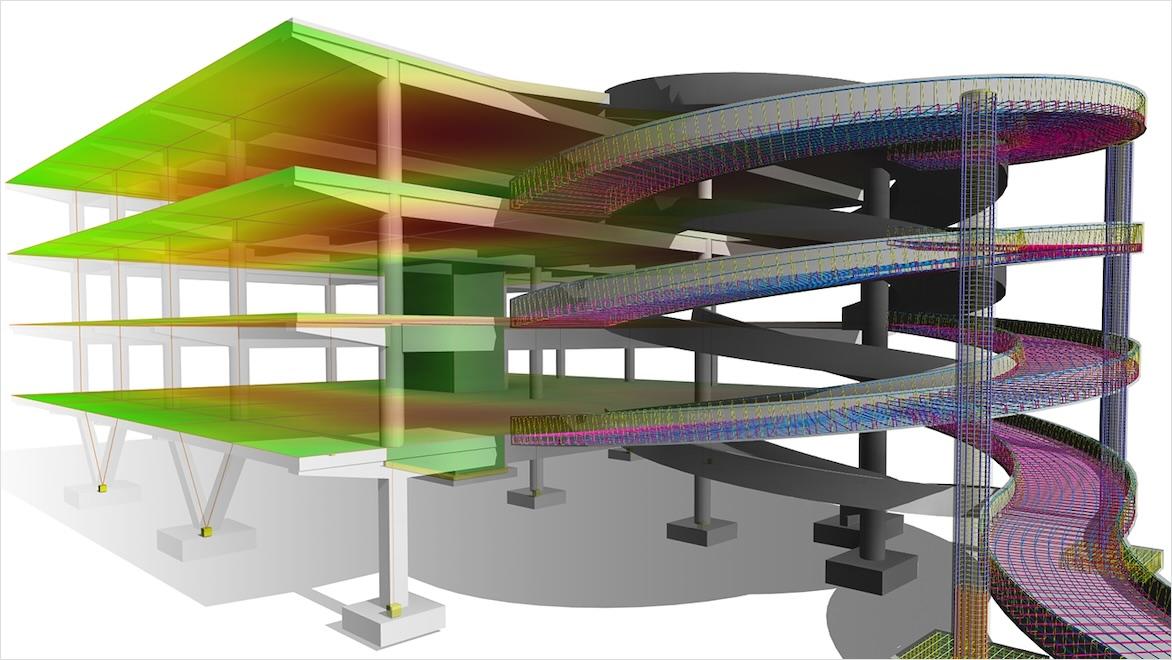
Reinforced concrete design is a specialized discipline within concrete engineering that involves enhancing the strength and durability of concrete elements by strategically incorporating reinforcement materials like steel bars or mesh. Concrete design engineers analyze structural requirements, choose suitable concrete mixes and reinforcement materials, adhere to building codes, and meticulously plan reinforced concrete design elements to create robust structures capable of withstanding various loads and environmental factors. This approach is widely employed in construction projects, offering strength, versatility, and longevity; it has become a fundamental practice for designing safe and enduring buildings, bridges, and infrastructure.
Concrete stands out as a commonly used construction material due to its exceptional strength, durability, versatility, and cost-effectiveness. It is renowned for its ability to withstand heavy loads, weather conditions, and time while offering fire resistance and adaptability for innovative design solutions. Concrete’s sustainability, thermal mass, sound insulation, and resistance to moisture contribute to its appeal. Concrete boasts utilitarian performance features, as well as cost-effectiveness and aesthetic potential, making it a mainstay in construction projects, from buildings to infrastructure, worldwide.
Concrete design software plays a crucial role in building information modeling (BIM) processes by integrating with BIM platforms, providing more accurate 3D modeling and structural analysis capabilities, ensuring code compliance, optimizing designs, offering visual representations for enhanced communication, generating comprehensive documentation, facilitating collaboration among project stakeholders, enabling conflict detection, and supporting sustainability assessments. The integration offered by concrete design software helps streamline design coordination, data sharing, and decision-making within the BIM environment, contributing to more efficient and well-informed construction projects.
Modern technology revolutionizes architectural concrete design by offering tools like CAD software for more precise modeling, structural analysis software for performance optimization, BIM for integrated coordination, 3D printing for customized elements, and simulations to predict behavior. Remote sensing and material testing technologies enhance site selection and quality control while augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) enable immersive visualization. Sustainability and green building tools promote eco-friendly concrete designs, and cloud collaboration platforms foster teamwork. Cost estimation, project management software, and robotics improve efficiency and precision, ultimately leading to safer, more sustainable, and innovative concrete structures.
Concrete is the second most consumed resource on Earth, second only to water, and it has many different uses that require careful concrete design, including:
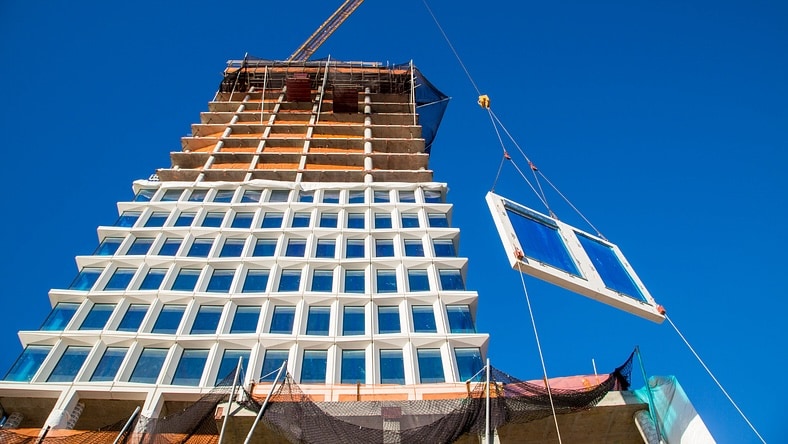
Concrete is the most common building material used around the world, from high-rise skyscrapers to single-story homes.
Due to their strength and weight absorption, concrete designs are frequently used for bridges. Reinforced and pre-stressed concretes are often used to ensure that the bridge is suitable for carrying heavy loads.
Durability, weather resistance, longevity, and fast build times all make concrete an easy choice for walls of all sizes.
As well as being a common sight above ground, concrete designs for sewage and water systems, reservoirs, and other infrastructure have proliferated around the globe.
Concrete design software offers many benefits to engineers, architects, and construction professionals involved in the design and analysis of concrete structures, including:
Concrete design software automates complex calculations and design processes, reducing the time and effort required for manual calculations.
Concrete software helps engineers explore multiple design options and quickly assess their impact on structural performance.
Architectural concrete design software typically adheres to local building codes and international standards, ensuring that designs are compliant with regulatory requirements.
The software can perform clash-detection analyses by comparing 3D rebar models and checking for clashes between rebars, as well as clashes between reinforced concrete elements and other structural elements within the same BIM environment.
Many concrete design software platforms are cloud-based, enabling real-time collaboration among team members, regardless of their physical location.
Though both concrete design and stamped concrete design involve the use of concrete and a design element, they are very different processes. While concrete design refers to all tasks involved in planning and analyzing concrete structures before construction, stamped concrete design refers specifically to the creation of decorative designs on the outer surface of the concrete, for example, in tiles and paving slabs.
Cost is of course an important part of any concrete construction project—Autodesk’s concrete software can help you stay on top of finances at all stages of the process. Revit, for example, can be used to create extensive material takeoff schedules, generate reports for bidding, and estimate costs more accurately.
Powerful BIM and CAD tools for designers, engineers, and contractors, including Revit, AutoCAD, Civil 3D, Forma Site Design, and more
Plan, design, construct, and manage buildings with powerful tools for Building Information Modeling.
Cloud-based design co-authoring, collaboration, and coordination software for architecture, engineering, and construction teams. “Pro” enables anytime, anywhere collaboration in Revit, Civil 3D, and AutoCAD Plant 3D.
Whether it’s for client proposals, documents to meet regulations, or other needs, Autodesk’s concrete design software can rapidly generate in-depth reports and documentation relating to your project. Autodesk Construction Cloud is designed for document management, including version control, real-time collaboration, and document distribution, helping streamline your concrete design processes.
Gate Precast
A concrete precast company uses 3D-printed concrete design molds to bring an ambitious building facade to life.
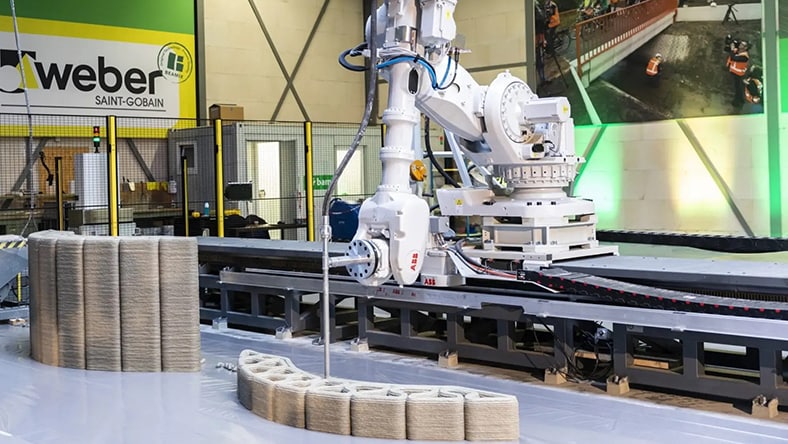
BAM & Saint-Gobain
Leading manufacturers save time and labor with sustainable, scalable, and affordable 3D concrete printing solutions.
Gate Precast
An architecture firm and concrete precast company collaborate with Revit to realize an innovative museum design.
Learn about the benefits of using BIM-centric solutions for reinforced-concrete design construction projects.
See how the Hone Structures project pioneers a new approach to sustainable concrete construction.
See how Concrete Collective takes a digital approach to concrete design molds and nesting with Fusion 360.
In reinforced concrete design, the Working Stress Method (WSM) assesses the safety of structures by comparing calculated stresses within concrete and steel to allowable limits, assuming elastic behavior within certain bounds. The Ultimate Strength Method (also known as Load and Resistance Factor Design, or LRFD) considers applied loads and the resistance capacity of materials such as concrete and steel to ensure safe designs. The Limit State Method (LSM) focuses on two key limit states: serviceability and ultimate strength, ensuring that reinforced concrete designs remain functional, durable, and safe under all expected loads and conditions.
Concrete mixtures come in various types to meet specific construction needs. Normal-strength concrete (NSC) is standard for most projects while high-strength concrete (HSC) offers increased strength. Ultra-high performance concrete (UHPC) excels in strength and durability. Self-consolidating concrete (SCC) flows without vibration, and fiber-reinforced concrete (FRC) resists cracking. Lightweight concrete is low density; high-density concrete is heavy. Shotcrete is pneumatically applied; pervious concrete is porous for drainage; and roller-compacted concrete (RCC) suits pavements. Shrinkage-compensating concrete minimizes cracks; colored concrete provides aesthetic options; and specialty mixes such as shrinkage-compensating and colored concrete cater to specific concrete design project needs.
Common concrete mix design requirements include the desired strength, durability, workability, and exposure conditions. Engineers must factor in the properties of aggregates, the type and content of cement, the water-cement ratio, and the inclusion of chemical admixtures to achieve the desired concrete properties. Proportions of these components are optimized to meet project specifications while ensuring cost-effectiveness and maintaining workability. Quality control measures, including material testing and trial mixes, are integral to ensuring the concrete design mix meets project requirements. Concrete design software can help you make short work of these calculations and reports.